
Top 125 + Parasitic nutrition in animals examples
The following points highlight the seven important modes of nutrition in Protozoa. The modes are: 1. Holozoic or Zoo-Trophic Nutrition 2. Pinocytosis 3. Autotrophic or Holophytic Nutrition 4. Saprozoic Nutrition 5. Parasitic Nutrition 6. Coprozoic Nutrition 7. Mixotrophic Nutrition. Nutrition: Mode # 1. Holozoic or Zoo-Trophic Nutrition: Majority of Protozoa nutrite holozoically, i.e., like.

Parasitic plants—A CuRe for what ails thee Science
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship, or long-term relationship between two species, where one member, the parasite, gains benefits that come at the expense of the host member. The word parasite comes from the Latin form of the Greek word παράσιτος (parasitos), meaning "one who eats at the table of another". Types of Parasitism

PARASITIC ROOTS YouTube
This kind of nutrition is found mainly in non-parasitic animals—simple ones like Amoeba and complex ones like human beings. How Organisms Obtain Nutrition: Different organisms obtain food in different ways. Nutrition in unicellular organisms, like Amoeba, involves ingestion by the cell surface, digestion and egestion.

Parasites Classification Chart Poster Art for Social Justice Ricardo Levins Morales
Nutrition and Protozoa (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the seven important modes of nutrition in Protozoa. The modes are: 1. Holozoic or Zoo-Trophic Nutrition 2. Pinocytosis 3. Autotrophic or Holophytic Nutrition 4. Saprozoic Nutrition 5. Parasitic Nutrition 6. Coprozoic Nutrition 7.
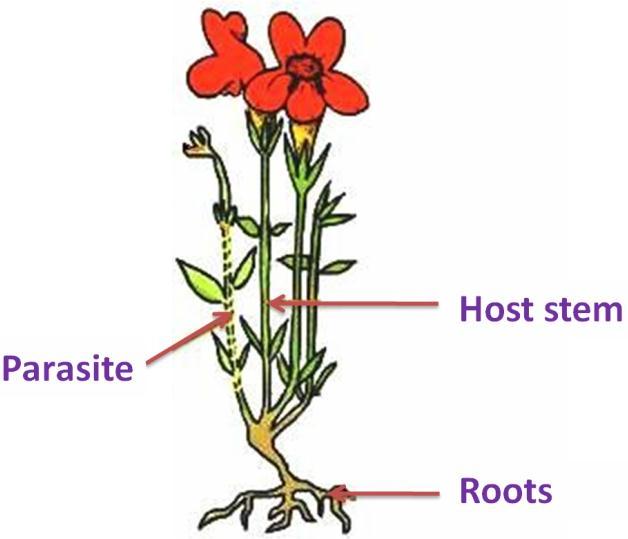
CBSE notes for biology class 7 nutrition in plants
Nutrition of parasitic protozoa: The mechanisms used by parasitic protozoa are almost are similar to that of their non-parasitic protozoa. Parasites inhabiting the intestine and blood have a distinct mouth through which food particles are ingested through the process of phagotrophy. The osmotrophic forms of protozoa are either coelozoic or.

NutritionThe Food Supplying System//Parasitic Nutrition in Cuscuta//10th class Biology Lessons
Solution Parasitic Nutrition Parasitic Nutrition is a mode of heterotrophic nutrition where an organism (known as a parasite) lives on the body surface or inside the body of another type of organism (known as a host). The parasite obtains nutrition directly from the body of the host.

Parasitic and Saprophytic Nutrition, biology Lecture Sabaq.pk YouTube
Get Ad-free version of Teachoo for ₹ 999 ₹499 per month. Heterotrophic mode of nutrition is further divided into 4 types: Parasitic Nutrition. Insectivorous Nutrition. Saprotrophic Nutrition. Symbiotic Nutrition.

PPT Nutrition PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1273391
1. Introduction. Intestinal parasitic infections are among the most common infectious diseases, affecting approximately 3.5 billion people every year and causing more than 450 million health problems, including diarrhoea, abdominal pain, undernutrition, general malaise and weakness, and impaired growth and physical development [1,2,3,4,5].Over 267 million preschool-age and 568 million school.

Parasitic Nutrition , Biology Lecture Sabaq.pk YouTube
Helminth Infection and Metabolic Diseases. It is estimated that one third of the world's population is infected with parasitic helminths with the greatest burden in underdeveloped nations particularly Nigeria and the Congo ().Nutrients are cofactors and activators for the developing immune system and malnutrition as well as bacterial co-infections are frequent in these developing areas and.
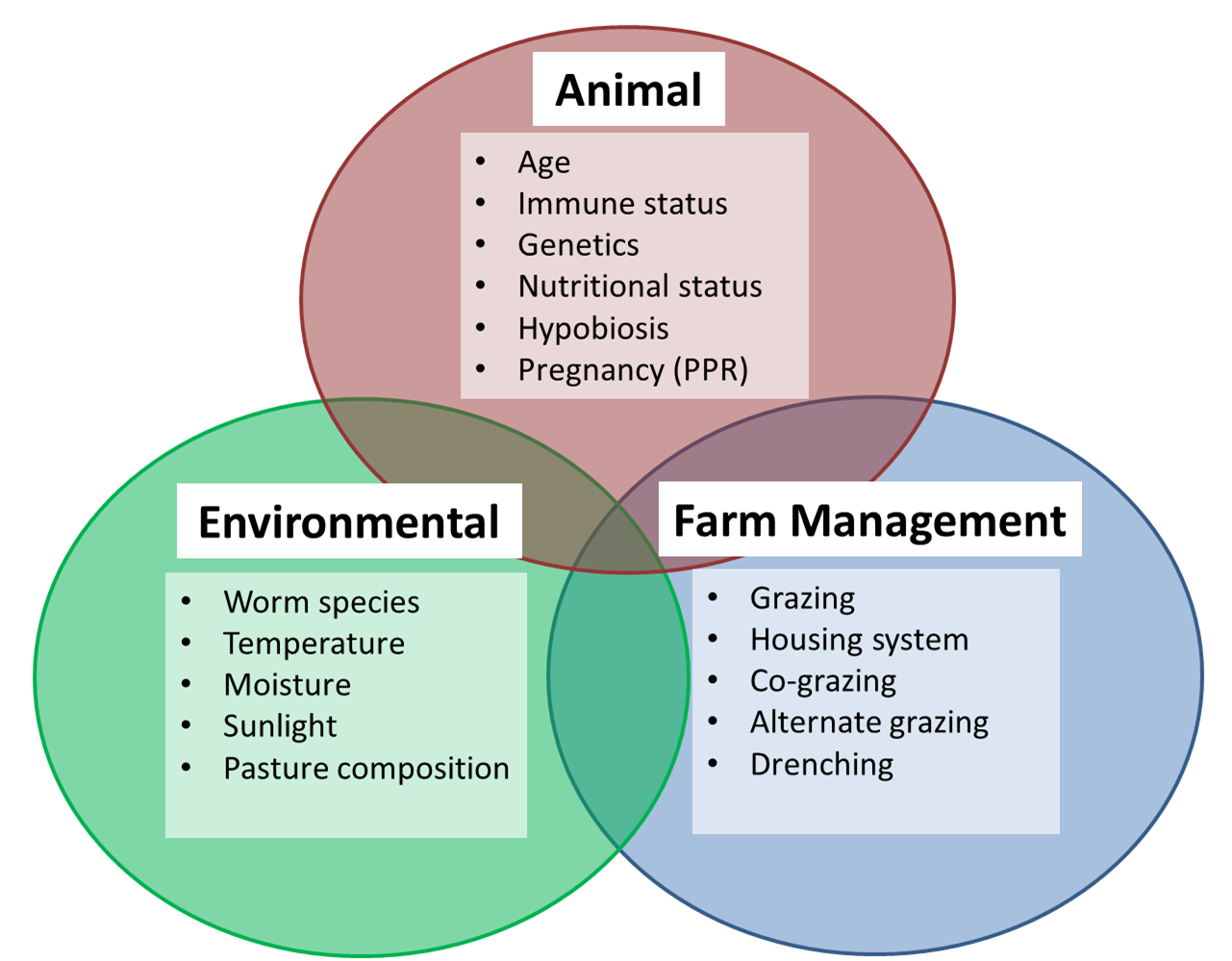
Farm Health Online Animal Health and Welfare Knowledge Hub Parasitic Gastroenteritis in
Review the below Heterotrophic nutrition diagram how autotrophs produce food and heterotrophs use them as food to survive.. Parasitic Nutrition; Saprophytic nutrition: Organisms receive nutrients from dead and decomposing organic substances in this way of nutrition. Saprophytes are the name given to these creatures. Yeast is an example.

Describe parasitic nutrition.! No spam Brainly.in
Secondly, in terms of the nutritional cost of an infection to a parasitised host. Thirdly, in terms of the feeding, nutrition and metabolism of parasites. Finally, in terms of damage to the tissues of the host caused by parasites. Two other sections deal briefly with the transmission of parasites in food and the effects of food on parasites.
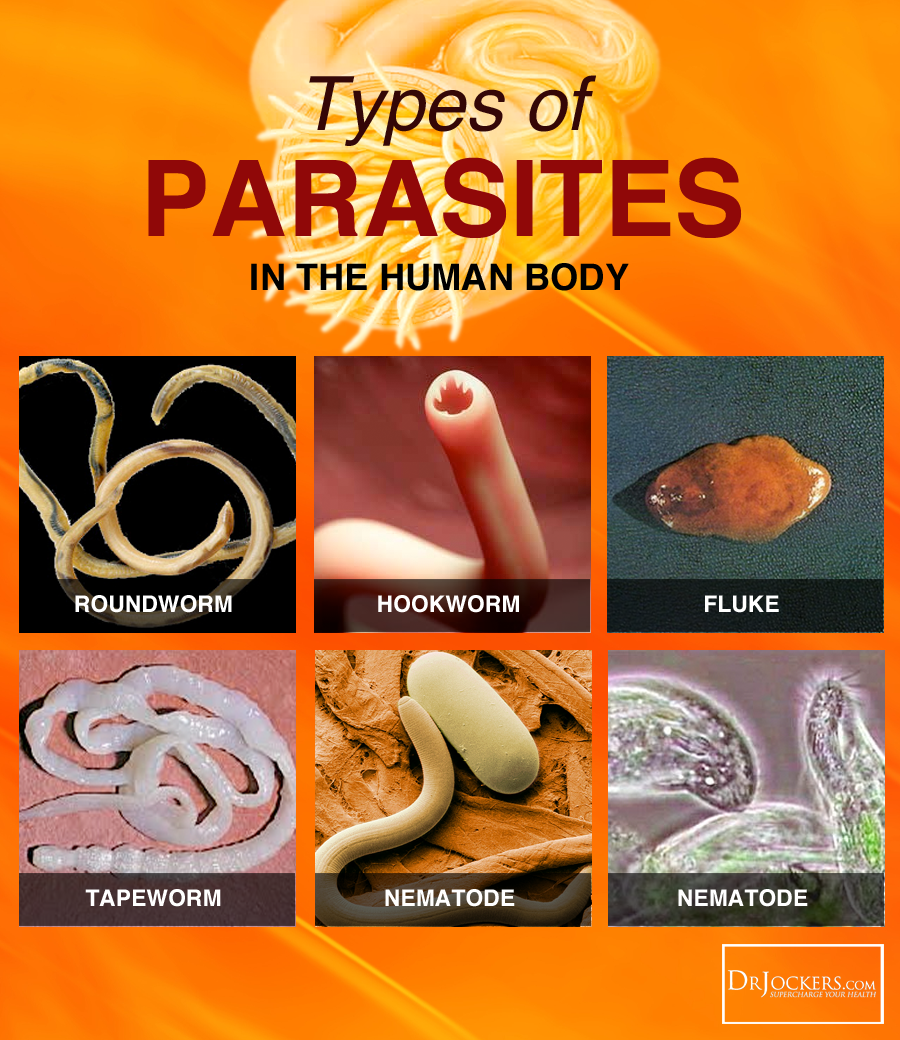
What Type of Parasites do You Have?
Most parasitic protozoa in humans are less than 50 μm in size. The smallest (mainly intracellular forms) are 1 to 10 μm long, but may measure 150 μm. Protozoa are unicellular eukaryotes. As in all eukaryotes, the nucleus is enclosed in a membrane.

Mode of Nutrition in Fungi Saprophytic, Parasitic, Symbiotic and Predatory YouTube
Heterotrophic nutrition can be one of three types - holozoic, saprophytic or parasitic. Holozoic nutrition can be seen in most vertebrates and some unicellular organisms like the amoeba. Saprophytic nutrition is where the organisms feed on dead and decaying matter. Examples include bacteria and fungi. Parasitic nutrition is where an organism.

PPT NUTRITION AND RESPIRATION PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID235271
Fungal and bacterial saprotrophs are referred to as saprophyte, while animal saprotrophs are called as saprozoites. Parasites are organisms, that live in or on other living organisms (called as the host) generally receiving shelter and deriving nutrients from it. The parasites may cause harm to the host plant. Thus, the correct options ae A and C.

Body Harvest — Parasitic Slavery Audio CD
Parasitic nutrition is a mode of heterotrophic nutrition where a parasitic organism lives on the body surface or inside the body of another type of organism (a host) and gets nutrition directly from the body of the host. Since these parasites derive nourishment from their host, this symbiotic interaction is often harmful to the host.

PPT Modes of Nutrition PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2959529
Parasitism is a kind of symbiosis, a close and persistent long-term biological interaction between a parasite and its host. Unlike saprotrophs, parasites feed on living hosts, though some parasitic fungi, for instance, may continue to feed on hosts they have killed.